HYPOTONIA
Hypotonia: Diagnosis & Treatment at Mir Neurology
What is Hypotonia?
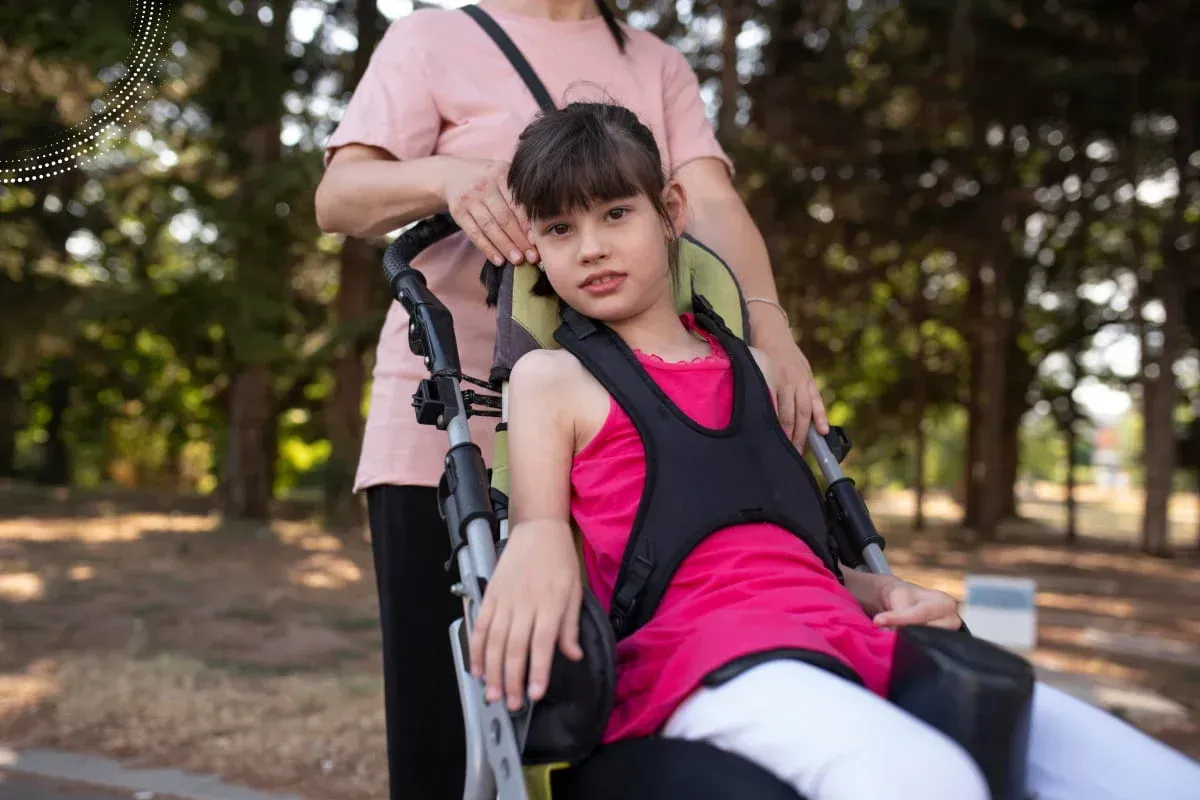
Hypotonia, commonly known as low muscle tone, is a neurological condition in which muscles have reduced resistance to passive movement. Muscle tone is different from muscle strength. Individuals with hypotonia may have normal strength but appear “floppy” or have difficulty maintaining posture and coordinated movements.
Hypotonia can affect infants, children, and adults, and its impact ranges from mild coordination difficulties to significant motor delays, depending on the underlying cause. At Mir Neurology, we provide comprehensive evaluation and individualized treatment plans to help patients improve function, mobility, and quality of life.
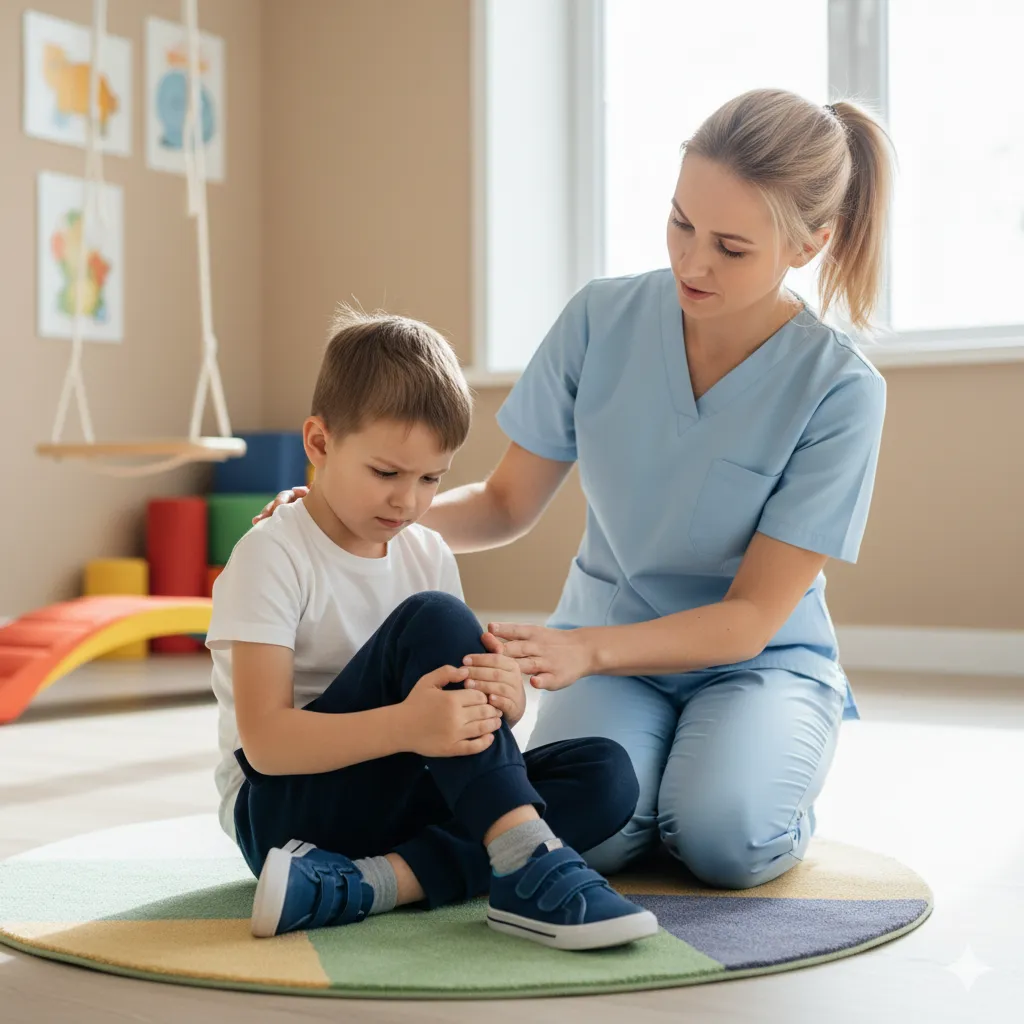
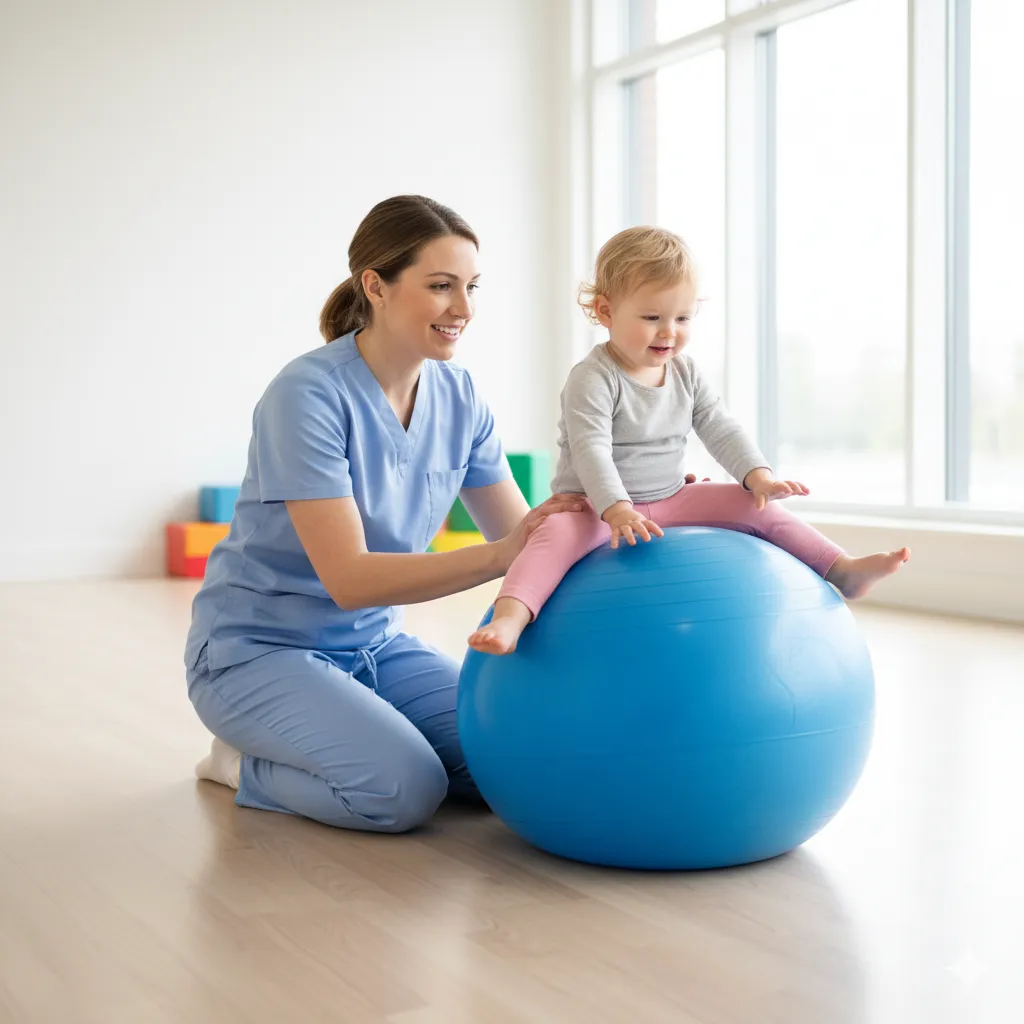


Symptoms of Hypotonia
Hypotonia manifests differently depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
Floppy or loose muscles: Difficulty holding the head up or maintaining body position.
Delayed motor milestones: Challenges with activities like late sitting, crawling, standing, or walking.
Weakness or fatigue: Lack of muscle strength, particularly in the trunk and limbs. Trouble maintaining upright posture
Reduced reflexes: Diminished or absent reflex responses when testing muscle activity.
Poor posture: Difficulty maintaining an upright or stable posture.
Difficulty with fine motor tasks: Struggles with tasks such as gripping objects, buttoning clothes, or writing.
Joint hypermobility: Overly flexible joints due to weak supporting muscles.
Causes of Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a sign, not a diagnosis, and may result from several underlying conditions:
1. Genetic Disorders
Conditions such as Down syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome are associated with hypotonia and may affect muscle tone from birth or early infancy.
2. Neurological Conditions
Cerebral palsy, spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), and muscular dystrophies can lead to hypotonia due to nerve or muscle dysfunction.
Brain injuries or developmental brain abnormalities can also impact motor control and muscle tone.


3. Metabolic or Hormonal Disorders
Disorders like hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) and mitochondrial diseases can contribute to low muscle tone.
4. Premature Birth
Premature infants often have underdeveloped muscles and nervous systems, which can result in hypotonia. This is typically temporary but may persist in some cases.
5. Primary Muscle Disorders
Conditions such as congenital myopathies and muscular dystrophies can directly affect muscle structure and tone, leading to hypotonia.
6. Other Causes
Infections and toxic exposures during pregnancy or early childhood can also result in hypotonia.
Diagnosis of Hypotonia
Diagnosing hypotonia involves a thorough medical evaluation and various tests to determine the underlying cause of the condition. At Mir Neurology, we take a comprehensive approach to diagnosis:
1. Medical History and Physical Exam
A detailed review of your medical history and family history of any neurological or muscle disorders is essential.
A physical examination will include assessments of muscle strength, reflexes, posture, and coordination.
2. Genetic Testing
In some cases, genetic tests may be performed to identify underlying genetic conditions such as Down syndrome or other inherited disorders.
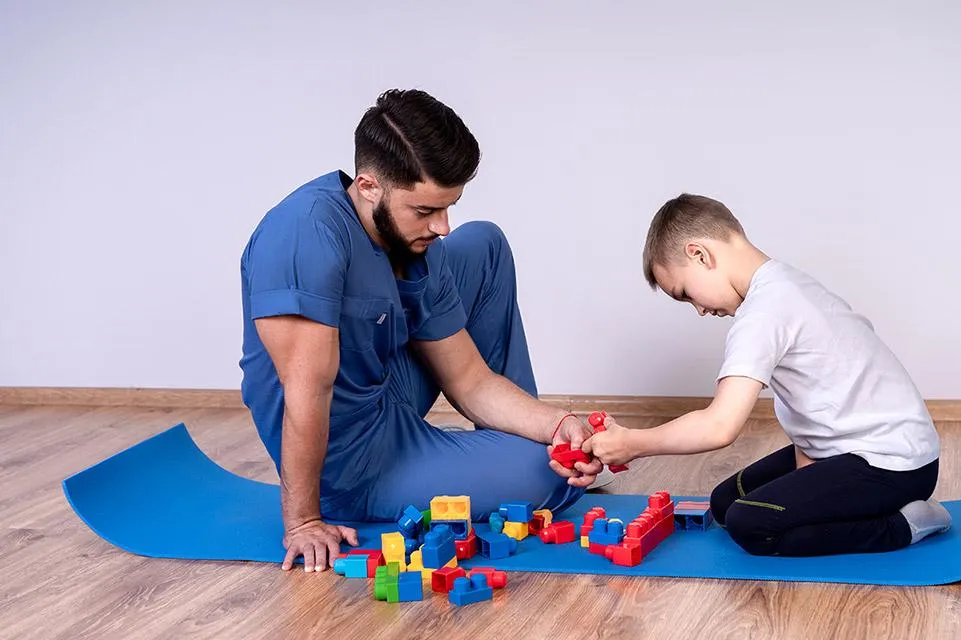

3. Imaging Studies
MRI or CT scans of the brain and spinal cord can help identify structural abnormalities, brain injuries, or other conditions that might contribute to hypotonia.
4. Blood Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to assess for metabolic, hormonal, or inflammatory conditions that could be causing hypotonia.
5. Electromyography (EMG)
An EMG may be used to measure electrical activity in muscles and nerves, helping to evaluate neuromuscular disorders such as muscular dystrophies, neuropathies, or disorders of neuromuscular transmission.
6. Muscle Biopsy
In some cases, a muscle biopsy may be performed to examine the muscle tissue for any abnormalities or signs of disease.
Treatment for Hypotonia
Treatment for hypotonia is highly individualized and depends on the underlying cause of the condition. At Mir Neurology, we collaborate with you to create a personalized treatment plan aimed at improving muscle tone, strength, and motor function.
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for hypotonia. Therapists will guide patients through exercises designed to strengthen muscles, improve coordination, and develop motor skills.
Postural training and balance exercises can also be beneficial to help manage daily activities.
2. Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy can help individuals with hypotonia improve fine motor skills necessary for daily tasks such as eating, dressing, or writing.


3. Speech Therapy
If hypotonia affects the muscles used for speaking or swallowing, speech therapy may be needed to help improve communication and ensure safe eating and drinking.
4. Medications
Medications are used to treat the underlying cause of hypotonia rather than hypotonia itself. For example:
Thyroid hormone replacement for hypothyroidism
Disease-specific treatments for metabolic or neuromuscular disorders
5. Orthotic Devices
Braces or splints may be used to help stabilize joints or provide support for weaker muscles, improving mobility and posture.
6. Surgery
In rare cases, surgical interventions may be needed to correct structural abnormalities or relieve pressure on the muscles or nerves that are contributing to hypotonia.
7. Supportive Care
Nutritional support may be important for individuals with severe hypotonia, particularly in young children who may have difficulty feeding due to weak muscles.
Family counseling and support groups can provide emotional and social support for families managing hypotonia.
Living with Hypotonia
With early diagnosis, appropriate therapy, and ongoing support, many individuals with hypotonia lead active and fulfilling lives. Early intervention is especially important in children to maximize developmental outcomes.
At Mir Neurology, we work closely with patients and families to address both the physical and emotional aspects of living with hypotonia, providing compassionate and evidence-based care at every stage.

Get Expert Help

If you or a loved one is experiencing memory loss or cognitive decline, early diagnosis is key to effective management. Consult with our neurology specialists for personalized assessment and care plans.
Our Locations
To learn more about our experience or discuss your treatment options, please call us at (301) 797-7600 or schedule a consultation today!
Get our wellness newsletter
Filter out the noise and nurture your inbox with health and wellness advice that’s inclusive and rooted in medical expertise.
Contact Us
Complaint and Queries
(301) 517-7636
About | Careers
© Copyright 2026. Mir Neurology. All Rights Reserved.
A Part of Highland Healthy Living. Powered By CareSyncMarketing



